
Typically the host's immune system is relied upon to fight off viruses. Antiviral drugs are used to treat some types of viral infections. Treatment for viral infections typically involve medicines that treat the symptoms of an infection and not the virus itself. These cancer viruses are known to cause cancers such as liver cancer, cervical cancer, and Burkitt's lymphoma. Some viruses can cause changes within host cells that result in the development of cancer. Viruses can cause persistent infections in which they go dormant and can be reactivated at a later time.

Pathogenic bacteria that cause disease produce toxins that destroy cells. Bacteria: While most bacteria are harmless and some are even beneficial to humans, other bacteria are capable of causing disease.
3 bacteria shapes full#
The largest viruses known, the pandoraviruses, are about 1000 nanometers or a full micrometer in size.

They generally range in size from 20-400 nanometers in diameter. Some viruses, such as bacteriophages, have complex shapes which include the addition of a protein tail attached to the capsid with tail fibers extending from the tail. Viruses typically have spherical (polyhedral), rod-shaped, or helically shaped capsids.

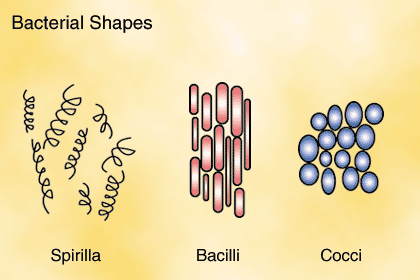
Viruses: The size and shape of viruses are determined by the amount of nucleic acid and proteins they contain.Considered the world's largest bacteria, Thiomargarita namibiensis can reach up to 750,000 nanometers (0.75 millimeters) in diameter. The largest bacterial cells are visible with the naked eye. Bacteria typically range in size from 200-1000 nanometers (a nanometer is 1 billionth of a meter) in diameter. Common bacterial cell shapes include cocci (spherical), bacilli (rod-shaped), spiral, and vibrio. Bacteria: Bacteria can be found in a variety of shapes and sizes.Viruses rely solely on a host for replication. While they contain genetic material, they don't have a cell wall or organelles necessary for energy production and reproduction. non-enveloped viruses typically enter a cell by endocytosis and exit by exocytosis or cell lysis.Īlso known as virions, virus particles exist somewhere between living and non-living organisms. This envelope helps the virus enter a new cell by fusion with the cell's membrane and helps it exit by budding. Some viruses have an additional membrane called an envelope that is composed of phospholipids and proteins obtained from the cell membrane of a previously infected host cell. Viruses: Viruses are not considered cells but exist as particles of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) encased within a protein shell.These organelles perform vital functions that enable bacteria to obtain energy from the environment and to reproduce. Bacterial cells contain organelles and DNA that are immersed within the cytoplasm and surrounded by a cell wall. Bacteria: Bacteria are prokaryotic cells that display all of the characteristics of living organisms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
